The efficiency of field service operations can make or break a company’s success. Field Service Management (FSM) software has become an essential tool for businesses that rely on a mobile workforce, helping to streamline operations, improve customer experience, and enhance service delivery. Fortunately, numerous options are available, including several free field service management software solutions that can meet the needs of various organizations. This article will delve into the best options to choose from and provide an overview of what FSM software entails, who requires a free field service management software, and what important features to look for.
What Is Free Field Service Management Software?
Free field service management software provides businesses with tools to automate and streamline various aspects of field service operations without incurring software costs. These free field service management software tools allow users to manage work orders, schedule appointments, assign technicians, track inventory, and communicate efficiently with clients and team members.
This free field service management software increases productivity and directs focus toward customer satisfaction. By eliminating manual processes and reducing paperwork, organizations can optimize their field services, ensuring quicker response times and improved service delivery. The term best free field service management software encompasses software options that are both cost-effective and feature-rich, catering to small and medium-sized businesses aiming for efficiency without the financial burden.
Who Needs Field Service Management Tools
Field Service Management (FSM) tools have become indispensable in various industries that depend on field operations and mobile workforces. The need for such tools arises from the desire to optimize workflows, improve communication, and enhance overall service delivery. Organizations looking to manage field operations efficiently can benefit greatly from FSM solutions. Below, we will explore in detail who needs these tools and how they can bring value across different sectors.
- HVAC Companies: Companies providing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) services are among the primary users of field service management tools. HVAC technicians often work in various locations, dealing with service calls for system installations, repairs, and maintenance. FSM software allows them to effectively schedule appointments, route technicians, and manage inventories, ensuring they have the necessary parts on hand for each job. The result is reduced downtime and enhanced customer satisfaction as service agents can complete tasks efficiently and transparently.
- Plumbing Services: Plumbing services often deal with emergencies that require immediate responses, making field service management tools vital. With the ability to prioritize jobs based on urgency, manage work orders, and efficiently dispatch technicians, plumbing companies can minimize response times and improve service levels. FSM tools also typically include customer relationship management (CRM) features that allow plumbing businesses to maintain comprehensive client records, track previous service calls, and even schedule follow-up maintenance. This leads to improved customer relationships and increased likelihood of repeat business.
- Electrical Contractors: Electrical contractors require a robust scheduling and project management framework due to the complexity of the projects they undertake. FSM software enables them to manage deadlines, allocate resources efficiently, and track the progress of multiple jobs simultaneously. This oversight is crucial for keeping costs down and ensuring compliance with industry regulations and safety standards. Furthermore, integration with billing and invoicing systems ensures accurate financial tracking, making it easier for electrical businesses to manage their bottom line.
- IT Service Providers: In today is tech-driven world, IT service providers play a critical role in maintaining technological operations for a myriad of businesses. They require FSM tools to handle service tickets, schedule onsite visits, and coordinate tasks among team members. Advanced FSM solutions can help track service performance metrics, allowing IT firms to measure response times and service quality, which are essential for competitive differentiation. With mobile access, technicians can log actions, update ticket status, and communicate with clients in real-time, enhancing the overall efficiency of IT operations.
- Landscaping and Grounds Maintenance Services: Companies in the landscaping and grounds maintenance sectors often juggle multiple clients, each requiring regular service. Field service management software aids in scheduling and dispatching, enabling these businesses to provide consistent service while optimizing routes for fuel efficiency. Tracking service quality through customer feedback forms integrated into the software can enhance the reputation of landscaping companies, driving new business through word-of-mouth and online reviews.
- Facility Management Firms: Facility management encompasses a wide range of services, from janitorial upkeep to maintenance of equipment and systems. FSM tools are essential for facility management companies to streamline operations, track maintenance schedules, and manage service requests from tenants or clients. By utilizing automated workflows, these firms can ensure that all tasks are documented and prioritized, leading to improved service delivery and tenant satisfaction.
- Equipment Repair and Maintenance Providers: Companies focused on equipment repair and maintenance in industries like manufacturing and construction often rely on FSM tools to manage service requests, inventory, and technician schedules. These tools enable quick response times and seamless coordination between the office and field staff. By effectively managing work orders and providing technicians with access to crucial equipment details and service history, businesses can perform repairs quickly and efficiently, thereby reducing equipment downtime in client operations.
- Delivery and Logistics Companies: In the logistics and delivery sector, timely service and efficiency are paramount. FSM tools help routing, scheduling, and tracking deliveries in real time. With integrated GPS tracking and route optimization, LLCs can reduce fuel expenses, speed up delivery times, and enhance customer service. The data amassed in these systems also provides valuable insights into operational bottlenecks, enabling continuous improvement over time.
- Home and Commercial Cleaning Services: Cleaning services, whether residential or commercial, need to manage multiple jobs for various clients efficiently. Field service management tools assist in scheduling jobs, dispatching staff, and managing customer preferences and feedback. This organization facilitates a higher level of service consistency while helping cleaning providers make data-driven decisions about workforce management, customer outreach, and job pricing.
- Telecommunications Providers: Telecommunications companies often have field technicians who install and maintain communication lines, internet connections, and other infrastructure. FSM tools allow them to efficiently manage these teams, schedule installations or repairs, and handle customer interactions smoothly. The agile capabilities of field service management also mean telecommunications companies can quickly adapt to changing schedules and customer demands, ensuring a high level of service reliability.
Each sector benefits from the ability to streamline operations, enhance scheduling and dispatching, and improve customer engagement. By configuring FSM software to meet their specific needs, organizations across these industries can enhance their operational efficiencies, reduce costs, and improve overall service quality, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. As businesses continue to evolve and expand their services, the importance of effective free open source field service management software tools will only continue to grow.
5 Important Things To Look For In Field Service Management Solutions
When considering a field service management (FSM) solution, businesses must evaluate various features and functionalities to ensure they select the software that best meets their operational needs. An effective FSM solution will not only streamline workflows but also enhance customer satisfaction and improve overall efficiency. Here are five critical aspects to look for when choosing field service management software:
- User-Friendly Interface: Choose software with an intuitive, easy-to-navigate design. A user-friendly interface ensures that technicians and office staff can quickly learn to use the system, maximizing productivity and minimizing frustration.
- Work Order Management: Look for solutions that enable seamless creation, assignment, and tracking of work orders. Key features include categorization, prioritization, and real-time status monitoring to enhance communication and responsiveness.
- Scheduling and Dispatching: Effective scheduling tools are essential. Opt for FSM solutions that offer drag-and-drop scheduling, calendar views, and real-time updates, along with GPS integration to optimize routes and resource allocation.
- Mobile Access: Ensure the software provides mobile applications or responsive web interfaces that allow field technicians to access work orders, update job statuses, and communicate with the back office in real time, even when offline.
- Integrations: Choose FSM solutions that can seamlessly integrate with existing business systems, such as CRM and accounting software. Effective integrations streamline workflows, enhance data exchange, and improve overall operational efficiency.
By focusing on these five critical aspects, you can select a field service management solution that meets your organization’s needs and enhances performance.
The 10 Best Free Field Service Management Software Programs
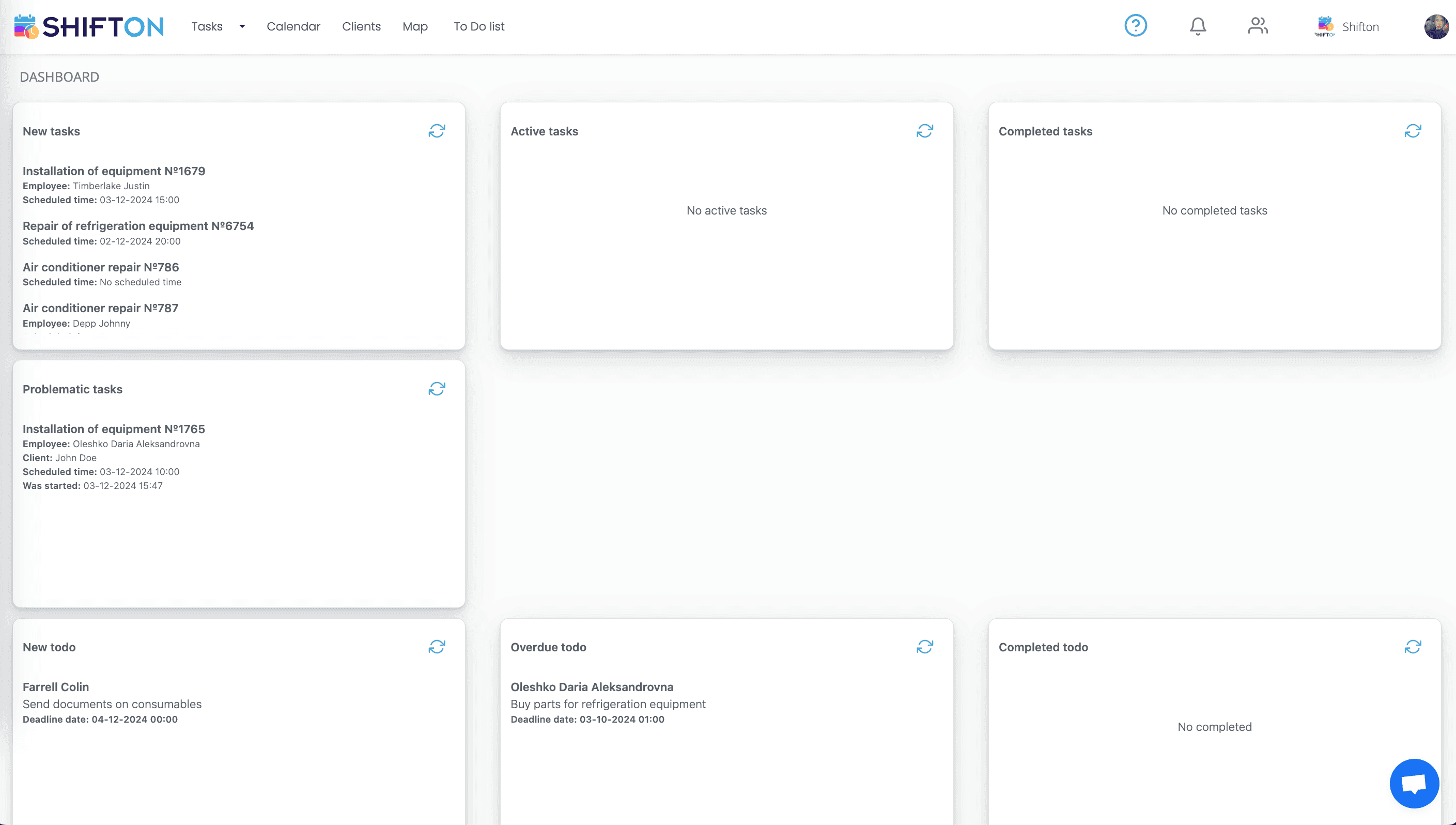
1. Shifton Service — Best Free Field Service Management Software
Shifton Service is the leading free field service management software designed specifically for businesses looking to streamline their service delivery. It offers tools to manage work orders, schedules, and technician assignments efficiently. Features:
- Work Order Management: Easily create, assign, and track work orders in real-time.
- Scheduling: Drag-and-drop calendar feature for efficient scheduling of jobs.
- Mobile Access: Technicians can access job details and update statuses on the go.
- Customer Database: Maintain client information and service history for personalized service.
Shifton Service can integrate with various third-party applications, including CRM systems, accounting software, and communication tools, to enhance workflow efficiency
2. Connecteam
Connecteam is an all-in-one field service management software that focuses on task management, team collaboration, and reporting. It is suitable for businesses of all sizes looking to improve efficiency. Features:
- Task Management: Create tasks and assign them to team members with deadlines.
- Time Tracking: Monitor employee hours and productivity with a built-in time clock.
- Communication Tools: Chat features allow for instant communication among team members.
- Reporting: Generate insightful reports to analyze performance metrics.
Connecteam offers integrations with popular tools like Zapier, QuickBooks, and Google Drive, enabling seamless data flow between platforms.
3. JotForm
JotForm provides customizable forms and workflow automation for field service management. It allows businesses to collect data efficiently, streamline operations, and ensure accuracy in field service processes. Features:
- Custom Forms: Build and customize forms with drag-and-drop functionality.
- Data Collection: Capture customer information, feedback, and service requests easily.
- Approval Workflows: Automate approval processes for faster service delivery.
- Mobile-Friendly: Access forms and data collection tools from mobile devices.
JotForm supports integration with a range of applications, including Google Sheets, Salesforce, and PayPal, enhancing its functionality across business operations.
4. Budibase
Budibase is an open-source low-code platform for building custom internal tools, including field service management applications. It allows businesses to automate workflows and manage data effectively. Features:
- Custom Application Development: Build tailored applications specific to field service needs.
- Automated Workflows: Streamline processes by automating repetitive tasks.
- Database Management: Manage and query data easily, ensuring accuracy and availability.
- User Management: Control user permissions and access settings for data security.
Budibase can integrate with various API-driven platforms, including Google Workspace and Slack, making it easy to incorporate into existing systems.
5. Miracle Service
Miracle Service is a comprehensive field service management solution designed for service-oriented businesses. It offers tools for managing service requests, technician dispatch, and billing. Features:
- Service Order Management: Keep track of service requests from initiation to completion.
- Field Technician Dispatch: Optimize routes and dispatch jobs efficiently to technicians.
- Inventory Control: Manage inventory levels and track parts and products used in services.
- Customer Portal: Allow customers to view service history and submit requests.
Miracle Service integrates with various accounting and ERP solutions like QuickBooks and Sage, providing a unified approach to managing service operations.
6. ServiceM8
ServiceM8 is an intuitive cloud-based field service management software that helps small businesses manage their operations more efficiently. It focuses on scheduling, invoicing, and customer relationship management. Features:
- Scheduling & Dispatching: Simple drag-and-drop scheduling and automated reminders.
- Invoicing: Generate professional invoices and accept payments on-site.
- Client Management: Keep track of customer information and service history.
- Mobile App: Comprehensive features available through a mobile application for technician convenience.
ServiceM8 integrates with various applications, including accounting software like Xero, and has a REST API for additional custom integrations.
7. Trinetra iWay
Trinetra iWay is an efficient field service management software that enables businesses to optimize operations through GPS tracking, route optimization, and work order management. Features:
- Live Tracking: GPS tracking of field technicians for real-time visibility.
- Route Optimization: Optimize routes to reduce travel time and increase productivity.
- Work Order Management: Streamlined process for creating and managing work orders.
- Reporting and Analytics: Comprehensive reporting tools to track performance metrics.
Trinetra iWay can integrate with popular GPS and mapping services, alongside CRM and project management tools.
8. Odoo
Odoo is a powerful suite of open-source applications that includes modules for project management, CRM, sales, and field service management. It is designed for companies looking for an integrated business solution. Features:
- Integrated Modules: Seamless integration between field service management and other business functions.
- Invoicing and Payments: Easily manage billing and transactions.
- Customizable Dashboards: Visualize data with tailored dashboards for quick insights.
- Mobile Support: Access all features via mobile devices.
Odoo integrates with eCommerce platforms, accounting software, and various third-party apps, making it a versatile choice for many businesses.
9. Delta Sales App
The Delta Sales App is designed for businesses to manage their sales and field service tasks effectively. It merges sales tracking with field service management to ensure customer satisfaction.
Features:
- Sales Management: Track leads, customer interactions, and sales progress.
- Field Service Management: Schedule and manage service requests alongside sales activities.
- Reporting Tools: Generate reports on sales performance and service efficiency.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Maintain relationships and follow up on leads effectively.
The Delta Sales App integrates with other sales and marketing platforms, enhancing capabilities and collaboration between departments.
10. BuildOps
BuildOps is a robust cloud-based platform specifically tailored for field service businesses in the construction and maintenance industries. It focuses on streamlining processes and enhancing operational efficiency. Features:
- Job Management: Track jobs from start to finish with task assignments and updates.
- Scheduling: Eliminate scheduling conflicts and optimize technician assignments.
- Inventory Management: Monitor inventory and manage stock levels efficiently.
- Financial Reporting: Robust financial tools to track costs and improve budgeting.
BuildOps integrates with various accounting and workflow management tools, ensuring that all aspects of the business can work together seamlessly.
Comparison Chart of the Best Free Field Service Management Software
Here is a comparison chart of the best free field service management software based on the descriptions, features, and integrations previously provided.
| Software | Description | Key Features | Integration Options |
Shifton Service | Best free option for managing service delivery. | Live Tracking Scheduling Mobile Access Customer Database | Integrates with Zapier, QuickBooks, and various CRM, accounting tools, and communication apps. |
Connecteam | All-in-one tool focusing on task management and team collaboration. | Task Management Time Tracking Communication Tools Reporting | Integrates with Zapier, QuickBooks, Google Drive, and others. |
JotForm | Customizable forms for efficient data collection and workflow automation. | Custom Forms Data Collection Approval Workflows Mobile-Friendly | Integrates with Google Sheets, Salesforce, PayPal, and more. |
Budibase | Open-source low-code platform for building custom applications. | Custom Application Development Automated Workflows Database Management User Management | API-driven integrations with Google Workspace, Slack, etc. |
Miracle Service | Comprehensive solution for service-oriented businesses. | Service Order Management Field Technician Dispatch Inventory Control Customer Portal | Integrates with QuickBooks, Sage, and other accounting/ERP solutions. |
ServiceM8 | Cloud-based software for small businesses focusing on scheduling and billing. | Scheduling & Dispatching Invoicing Client Management Mobile App | Integrates with Xero and offers REST API for custom integrations. |
Trinetra iWay | Efficient management via GPS tracking and route optimization. | Live Tracking Route Optimization Work Order Management Reporting | Integrates with GPS and mapping services, as well as CRM tools. |
Odoo | Open-source suite with modules for integrated business solutions. | Integrated Modules Invoicing and Payments Customizable Dashboards Mobile Support | Integrates with various eCommerce platforms, accounting software, and third-party apps. |
Delta Sales App | Merges sales tracking with field service management. | Sales Management Field Service Management Reporting Tools CRM | Integrates with sales and marketing platforms for enhanced collaboration. |
BuildOps | Tailored for construction and maintenance industries. | Job Management Scheduling Inventory Management Financial Reporting | Integrates with accounting and workflow management tools. |
This chart provides a concise comparison of the various software options, showcasing their unique features and integration capabilities, allowing potential users to make informed decisions about which tool best fits their needs.
Summing Up and Final Thoughts
In summation, free field service management software presents an excellent opportunity for businesses looking to improve their field service operations without hefty software costs. As we have explored, numerous high-quality options exist, each offering unique features and capabilities to cater to specific needs.
Field Service Management Considerations For Certain Businesses
Some considerations when choosing a free field service management software include the specific requirements of your industry, the size of your team, and the types of services you offer. Understanding these nuances allows businesses to select the software that best fits their operational needs.
What Are The Emerging Trends Of Field Service Management Software
As technology continues to advance, several trends are emerging in the field service management industry. These include the increased use of AI for predictive maintenance, mobile-enabled solutions for technicians, and enhanced customer service through real-time communication and feedback tools. Keeping an eye on these trends can help businesses stay ahead of the curve.
How Much Does Free Field Service Management Software Cost
While many free field service management software options are available, organisations must also consider the potential costs associated with scaling, additional features, or premium upgrades. However, selecting the best free field service management software that aligns with company goals can provide significant long-term savings and improvements in efficiency.
Ultimately, the right free open source field service management software can transform your business processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and improve your bottom line. As you embark on your search, remember the features and capabilities that matter most to your organization, and do not hesitate to explore the wide array of solutions available.