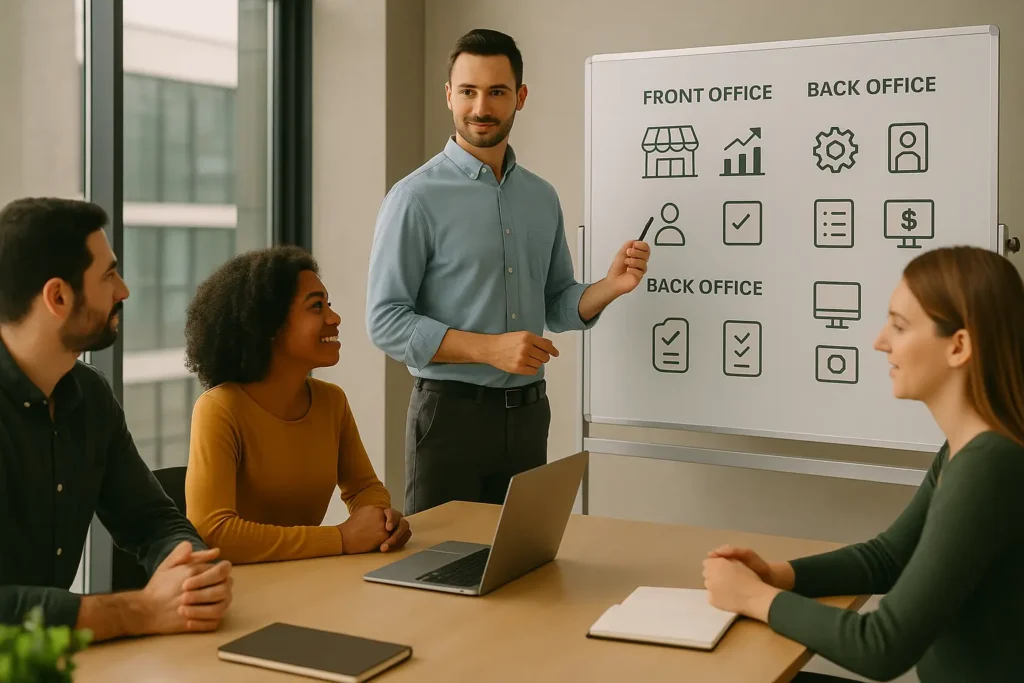
Running a business is like operating a machine. The front office is the visible part that interacts with customers, while the Backend Office is the hidden engine that ensures everything works smoothly. Even if clients never see it, this part of the company is critical for efficiency, accuracy, and growth.
In this article, we’ll explain what a backend office is, why it matters, what functions it performs, and how companies can manage it effectively.
What Is a Backend Office?
A backend office is the internal part of a business that focuses on administration, support, and operational continuity. Unlike the front office, which interacts with customers directly, the backend team works behind the scenes.
Examples of backend departments include:
Human resources (HR) – hiring, training, benefits.
Finance and accounting – payroll, invoices, budgeting.
IT support – maintaining digital systems, cybersecurity.
Operations management – logistics, supply chain, inventory.
Legal and compliance – ensuring the company follows laws and regulations.
While customers rarely see backend staff, their work impacts every interaction clients have with the company.
Why Businesses Need a Backend Office
Some entrepreneurs believe only sales and marketing matter because they generate revenue. But without strong backend operations, even the best sales strategy can fail. Here’s why backend offices are essential:
Operational efficiency – They reduce delays, manage schedules, and keep processes running.
Financial integrity – Accurate accounting prevents costly mistakes.
Employee satisfaction – HR ensures fair treatment, payroll accuracy, and professional development.
Technological stability – IT keeps systems secure and prevents downtime.
Legal protection – Compliance reduces risks of lawsuits or penalties.
In today’s highly competitive market, backend offices give businesses the foundation to scale without chaos.
The Role of Backend Office in Modern Companies
The backend office acts as the backbone of any organisation. It supports the customer-facing side by handling tasks employees and managers can’t do alone. This includes maintaining records, creating reports, ensuring smooth payroll, and preparing data for decision-making.
When managed well, backend operations boost productivity and allow front-line staff to focus on customers.
For example, if your sales team closes 100 deals in a month, the backend office ensures invoices are sent, payments are processed, new employees are hired to handle extra workload, and IT systems run smoothly. Without this support, growth would quickly collapse under pressure.
Key Backend Office Functions Every Business Needs
Every company’s backend office may look different, but most share these core functions:
1. Human Resources (HR)
Recruiting and onboarding new employees.
Conducting training and development.
Managing employee relations, benefits, and performance reviews.
A strong HR team reduces turnover, keeps employees motivated, and ensures compliance with labour laws.
2. Finance and Accounting
Preparing budgets and reports.
Handling payroll and tax compliance.
Managing invoices, expenses, and audits.
Finance departments ensure the company remains solvent, profitable, and legally compliant.
3. IT Support
Ensuring cybersecurity.
Updating and maintaining digital systems.
Providing technical help to employees.
Without IT, even simple tasks like email communication or order processing could break down.
4. Operations Management
Managing logistics and supply chains.
Monitoring inventory levels.
Coordinating daily workflows to avoid delays.
Good operations reduce waste, cut costs, and deliver products on time.
5. Compliance and Legal
Preparing contracts and agreements.
Ensuring labour law compliance.
Handling risk management and legal disputes.
Legal teams prevent costly mistakes and protect the company’s reputation.
Backend Office vs Front Office
It’s important to understand the difference between front and backend functions:
Front Office = customer-facing roles like sales, service, and marketing.
Backend Office = support roles like HR, finance, and IT.
One generates revenue directly, the other ensures stability and scalability. Together, they create a complete business system.
A practical example: A retail company’s sales team launches a major promotion. The backend team ensures inventory is ready, staff are scheduled, systems can handle extra demand, and finances track income. Without backend support, the campaign would fail.
Challenges of Managing a Backend Office
Despite its importance, backend management is not always easy. Companies face challenges such as:
High costs – maintaining specialised staff and systems can be expensive.
Complexity – multiple departments must coordinate effectively.
Technology updates – outdated systems reduce efficiency.
Data security – increasing cyber threats require strong protection.
Talent retention – backend roles are less visible, so employees may feel undervalued.
How to Optimise Backend Office Operations
Here are best practices to strengthen backend functions:
Use digital tools – Automate payroll, scheduling, and data entry.
Train employees – Skilled workers reduce errors and improve processes.
Maintain transparency – Share data across departments to improve decisions.
Outsource when needed – External providers can handle payroll or IT security more efficiently.
Invest in cybersecurity – Protecting data is critical for trust and compliance.
Centralise information – Using one platform avoids duplication and confusion.
The Future of Backend Office
Technology is reshaping backend operations. Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation tools are already changing how companies manage payroll, recruitment, and inventory. Cloud solutions make it easier for remote teams to access data securely.
Future trends include:
AI-driven HR – algorithms predicting candidate success.
Chatbots for HR and IT – faster employee support.
Blockchain for finance – safer, more transparent transactions.
Deeper analytics – better forecasts and reporting.
Companies that adapt to these technologies will be more competitive and resilient.
Real-World Example of Backend Office in Action
Imagine a growing e-commerce business. The front office team handles marketing campaigns and customer service. Orders skyrocket during the holiday season.
The backend office ensures:
HR hires temporary workers quickly.
IT strengthens website security and bandwidth.
Finance processes thousands of transactions without errors.
Operations manage warehouse logistics and shipping.
Compliance ensures all seasonal workers follow labour regulations.
This smooth collaboration allows the company to profit from high demand without collapsing under pressure.
Backend Office in Shifton
Shifton helps companies streamline workforce management, but it also plays a role in backend operations. With its scheduling, reporting, and automation features, Shifton reduces manual tasks in HR and operations, ensuring employees are in the right place at the right time.
By combining front-line scheduling with backend support, businesses can align strategy with execution, save time, and improve overall efficiency.
Conclusion
The backend office may not be visible to customers, but it is the hidden engine that drives business success. From HR and finance to IT and compliance, backend teams keep everything organised, secure, and efficient.
Companies that invest in their backend gain stronger stability, better employee satisfaction, and the ability to grow faster. With tools like Shifton, optimising backend operations becomes easier than ever.

 English (US)
English (US)  English (GB)
English (GB)  English (CA)
English (CA)  English (AU)
English (AU)  English (NZ)
English (NZ)  English (ZA)
English (ZA)  Español (ES)
Español (ES)  Español (MX)
Español (MX)  Español (AR)
Español (AR)  Português (BR)
Português (BR)  Português (PT)
Português (PT)  Deutsch (DE)
Deutsch (DE)  Deutsch (AT)
Deutsch (AT)  Français (FR)
Français (FR)  Français (BE)
Français (BE)  Français (CA)
Français (CA)  Italiano
Italiano  日本語
日本語  中文
中文  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  עברית
עברית  العربية
العربية  한국어
한국어  Nederlands
Nederlands  Polski
Polski  Türkçe
Türkçe  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский  Magyar
Magyar  Română
Română  Čeština
Čeština  Български
Български  Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά  Svenska
Svenska  Dansk
Dansk  Norsk
Norsk  Suomi
Suomi  Bahasa
Bahasa  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Tagalog
Tagalog  ไทย
ไทย  Latviešu
Latviešu  Lietuvių
Lietuvių  Eesti
Eesti  Slovenčina
Slovenčina  Slovenščina
Slovenščina  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Македонски
Македонски  Қазақ
Қазақ  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  বাংলা
বাংলা 

